Rails Form Drag and Drop Photo Uploader
Agile Storage Overview
This guide covers how to adhere files to your Agile Record models.
Later on reading this guide, yous volition know:
- How to adhere i or many files to a record.
- How to delete an attached file.
- How to link to an fastened file.
- How to apply variants to transform images.
- How to generate an image representation of a not-image file, such every bit a PDF or a video.
- How to transport file uploads directly from browsers to a storage service, bypassing your application servers.
- How to clean up files stored during testing.
- How to implement support for additional storage services.
 Capacity
Capacity
- What is Active Storage?
- Requirements
- Setup
- Disk Service
- S3 Service (Amazon S3 and S3-compatible APIs)
- Microsoft Azure Storage Service
- Google Deject Storage Service
- Mirror Service
- Public access
- Attaching Files to Records
-
has_one_attached -
has_many_attached - Attaching File/IO Objects
-
- Removing Files
- Serving Files
- Redirect mode
- Proxy way
- Authenticated Controllers
- Downloading Files
- Analyzing Files
- Displaying Images, Videos, and PDFs
- Lazy vs Immediate Loading
- Transforming Images
- Previewing Files
- Direct Uploads
- Usage
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) configuration
- Direct upload JavaScript events
- Example
- Integrating with Libraries or Frameworks
- Testing
- Discarding files created during tests
- Adding attachments to fixtures
- Implementing Support for Other Deject Services
- Purging Unattached Uploads
i What is Agile Storage?
Active Storage facilitates uploading files to a deject storage service similar Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure Storage and attaching those files to Agile Record objects. It comes with a local disk-based service for development and testing and supports mirroring files to subordinate services for backups and migrations.
Using Active Storage, an application can transform paradigm uploads or generate image representations of non-image uploads like PDFs and videos, and excerpt metadata from arbitrary files.
1.1 Requirements
Diverse features of Agile Storage depend on 3rd-political party software which Rails will not install, and must exist installed separately:
- libvips v8.six+ or ImageMagick for paradigm analysis and transformations
- ffmpeg v3.four+ for video previews and ffprobe for video/audio assay
- poppler or muPDF for PDF previews
Image analysis and transformations likewise require the image_processing gem. Uncomment it in your Gemfile, or add together it if necessary:
gem "image_processing" , ">= 1.2" Compared to libvips, ImageMagick is better known and more widely available. Nonetheless, libvips can exist up to 10x faster and eat one/10 the memory. For JPEG files, this can be further improved by replacing libjpeg-dev with libjpeg-turbo-dev, which is ii-7x faster.
Earlier you install and use tertiary-political party software, brand sure you empathize the licensing implications of doing so. MuPDF, in particular, is licensed under AGPL and requires a commercial license for some use.
two Setup
Active Storage uses iii tables in your awarding's database named active_storage_blobs, active_storage_variant_records and active_storage_attachments. Afterward creating a new application (or upgrading your application to Runway 5.2), run bin/rail active_storage:install to generate a migration that creates these tables. Use bin/rails db:migrate to run the migration.
active_storage_attachments is a polymorphic bring together table that stores your model'south class name. If your model's class name changes, you volition demand to run a migration on this tabular array to update the underlying record_type to your model's new class name.
If you lot are using UUIDs instead of integers as the primary key on your models you will need to change the column type of active_storage_attachments.record_id and active_storage_variant_records.id in the generated migration accordingly.
Declare Active Storage services in config/storage.yml. For each service your awarding uses, provide a proper name and the requisite configuration. The example below declares 3 services named local, test, and amazon:
local : service : Disk root : <%= Rails.root.join("storage") %> test : service : Disk root : <%= Rails.root.bring together("tmp/storage") %> amazon : service : S3 access_key_id : " " secret_access_key : " " bucket : " " region : " " # east.yard. 'us-east-ane' Tell Active Storage which service to use by setting Runway.application.config.active_storage.service. Because each environment will probable use a different service, it is recommended to practice this on a per-surroundings basis. To use the disk service from the previous example in the evolution surroundings, you would add the following to config/environments/development.rb:
# Store files locally. config . active_storage . service = :local To use the S3 service in production, y'all add the post-obit to config/environments/production.rb:
# Shop files on Amazon S3. config . active_storage . service = :amazon To use the examination service when testing, yous add the post-obit to config/environments/test.rb:
# Shop uploaded files on the local file system in a temporary directory. config . active_storage . service = :test Go on reading for more information on the congenital-in service adapters (e.grand. Deejay and S3) and the configuration they require.
Configuration files that are environment-specific will take precedence: in product, for example, the config/storage/production.yml file (if real) will take precedence over the config/storage.yml file.
It is recommended to use Rails.env in the saucepan names to further reduce the gamble of accidentally destroying production data.
amazon : service : S3 # ... bucket : your_own_bucket-<%= Rails.env %> google : service : GCS # ... bucket : your_own_bucket-<%= Track.env %> azure : service : AzureStorage # ... container : your_container_name-<%= Rails.env %> 2.1 Disk Service
Declare a Disk service in config/storage.yml:
local : service : Disk root : <%= Track.root.join("storage") %> two.two S3 Service (Amazon S3 and S3-compatible APIs)
To connect to Amazon S3, declare an S3 service in config/storage.yml:
amazon : service : S3 access_key_id : " " secret_access_key : " " region : " " bucket : " " Optionally provide customer and upload options:
amazon : service : S3 access_key_id : " " secret_access_key : " " region : " " bucket : " " http_open_timeout : 0 http_read_timeout : 0 retry_limit : 0 upload : server_side_encryption : " " # 'aws:kms' or 'AES256' Gear up sensible customer HTTP timeouts and retry limits for your application. In certain failure scenarios, the default AWS client configuration may crusade connections to be held for up to several minutes and lead to asking queuing.
Add the aws-sdk-s3 gem to your Gemfile:
gem "aws-sdk-s3" , require: false The core features of Agile Storage require the following permissions: s3:ListBucket, s3:PutObject, s3:GetObject, and s3:DeleteObject. Public access additionally requires s3:PutObjectAcl. If you take additional upload options configured such equally setting ACLs then additional permissions may be required.
If you want to use environment variables, standard SDK configuration files, profiles, IAM case profiles or task roles, you tin can omit the access_key_id, secret_access_key, and region keys in the case to a higher place. The S3 Service supports all of the authentication options described in the AWS SDK documentation.
To connect to an S3-compatible object storage API such as DigitalOcean Spaces, provide the endpoint:
digitalocean : service : S3 endpoint : https://nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com access_key_id : ... secret_access_key : ... # ...and other options There are many other options available. You tin can bank check them in AWS S3 Client documentation.
2.3 Microsoft Azure Storage Service
Declare an Azure Storage service in config/storage.yml:
azure : service : AzureStorage storage_account_name : " " storage_access_key : " " container : " " Add the azure-storage-blob gem to your Gemfile:
gem "azure-storage-hulk" , require: false 2.4 Google Cloud Storage Service
Declare a Google Deject Storage service in config/storage.yml:
google : service : GCS credentials : <%= Track.root.join("path/to/keyfile.json") %> projection : " " saucepan : " " Optionally provide a Hash of credentials instead of a keyfile path:
google : service : GCS credentials : type : " service_account" project_id : " " private_key_id : <%= Rails.awarding.credentials.dig(:gcs, :private_key_id) %> private_key : <%= Rails.application.credentials.dig(:gcs, :private_key).dump %> client_email : " " client_id : " " auth_uri : " https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth" token_uri : " https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token" auth_provider_x509_cert_url : " https://world wide web.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs" client_x509_cert_url : " " project : " " bucket : " " Optionally provide a Enshroud-Command metadata to set on uploaded assets:
google : service : GCS ... cache_control : " public, max-age=3600" Optionally use IAM instead of the credentials when signing URLs. This is useful if you are authenticating your GKE applications with Workload Identity, see this Google Cloud web log post for more information.
google : service : GCS ... iam : true Optionally use a specific GSA when signing URLs. When using IAM, the metadata server will be contacted to get the GSA email, but this metadata server is not always present (e.g. local tests) and yous may wish to use a non-default GSA.
google : service : GCS ... iam : true gsa_email : " foobar@baz.iam.gserviceaccount.com" Add the google-cloud-storage jewel to your Gemfile:
gem "google-cloud-storage" , "~> 1.xi" , crave: false 2.v Mirror Service
You lot can go along multiple services in sync by defining a mirror service. A mirror service replicates uploads and deletes across two or more than subordinate services.
A mirror service is intended to exist used temporarily during a migration between services in production. You tin get-go mirroring to a new service, re-create pre-existing files from the sometime service to the new, then go all-in on the new service.
Mirroring is not atomic. It is possible for an upload to succeed on the master service and fail on whatsoever of the subordinate services. Before going all-in on a new service, verify that all files take been copied.
Define each of the services y'all'd like to mirror as described above. Reference them by name when defining a mirror service:
s3_west_coast : service : S3 access_key_id : " " secret_access_key : " " region : " " bucket : " " s3_east_coast : service : S3 access_key_id : " " secret_access_key : " " region : " " bucket : " " production : service : Mirror master : s3_east_coast mirrors : - s3_west_coast Although all secondary services receive uploads, downloads are always handled by the primary service.
Mirror services are compatible with direct uploads. New files are straight uploaded to the chief service. When a directly-uploaded file is fastened to a record, a background job is enqueued to copy information technology to the secondary services.
2.six Public access
By default, Agile Storage assumes private access to services. This ways generating signed, single-use URLs for blobs. If you'd rather make blobs publicly attainable, specify public: true in your app'due south config/storage.yml:
gcs : &gcs service : GCS project : " " private_gcs : << : *gcs credentials : <%= Rails.root.bring together("path/to/private_keyfile.json") %> bucket : " " public_gcs : << : *gcs credentials : <%= Rail.root.join("path/to/public_keyfile.json") %> saucepan : " " public : true Make certain your buckets are properly configured for public admission. See docs on how to enable public read permissions for Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure storage services. Amazon S3 additionally requires that y'all have the s3:PutObjectAcl permission.
When converting an existing application to use public: true, make sure to update every individual file in the saucepan to be publicly-readable before switching over.
iii Attaching Files to Records
3.1 has_one_attached
The has_one_attached macro sets up a i-to-one mapping between records and files. Each record can have one file attached to it.
For example, suppose your application has a User model. If you desire each user to have an avatar, define the User model as follows:
class User < ApplicationRecord has_one_attached :avatar cease or if you are using Rails 6.0+, you can run a model generator command similar this:
bin / runway generate model User avatar :attachment You lot can create a user with an avatar:
<%= course . file_field :avatar %> class SignupController < ApplicationController def create user = User . create! ( user_params ) session [ :user_id ] = user . id redirect_to root_path end private def user_params params . require ( :user ). permit ( :email_address , :countersign , :avatar ) cease cease Call avatar.adhere to attach an avatar to an existing user:
user . avatar . attach ( params [ :avatar ]) Call avatar.attached? to determine whether a particular user has an avatar:
In some cases you might want to override a default service for a specific attachment. Y'all can configure specific services per zipper using the service option:
form User < ApplicationRecord has_one_attached :avatar , service: :s3 end Yous can configure specific variants per attachment by calling the variant method on yielded attachable object:
form User < ApplicationRecord has_one_attached :avatar do | attachable | attachable . variant :thumb , resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ] end terminate Phone call avatar.variant(:pollex) to get a thumb variant of an avatar:
<%= image_tag user . avatar . variant ( :pollex ) %> 3.2 has_many_attached
The has_many_attached macro sets up a one-to-many human relationship between records and files. Each tape tin take many files attached to information technology.
For example, suppose your application has a Bulletin model. If you desire each message to take many images, define the Message model as follows:
class Bulletin < ApplicationRecord has_many_attached :images end or if y'all are using Runway vi.0+, you lot can run a model generator command like this:
bin / runway generate model Message images :attachments You can create a message with images:
class MessagesController < ApplicationController def create message = Bulletin . create! ( message_params ) redirect_to message stop private def message_params params . crave ( :bulletin ). permit ( :title , :content , images: []) cease terminate Phone call images.attach to add together new images to an existing message:
@message . images . attach ( params [ :images ]) Call images.attached? to determine whether a particular message has whatever images:
@message . images . attached? Overriding the default service is done the same mode as has_one_attached, by using the service pick:
class Message < ApplicationRecord has_many_attached :images , service: :s3 end Configuring specific variants is done the same manner equally has_one_attached, by calling the variant method on the yielded attachable object:
class Message < ApplicationRecord has_many_attached :images do | attachable | attachable . variant :thumb , resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ] end end three.3 Attaching File/IO Objects
Sometimes you need to attach a file that doesn't arrive via an HTTP asking. For example, yous may want to attach a file yous generated on deejay or downloaded from a user-submitted URL. You may too desire to attach a fixture file in a model examination. To do that, provide a Hash containing at least an open up IO object and a filename:
@message . images . attach ( io: File . open ( '/path/to/file' ), filename: 'file.pdf' ) When possible, provide a content type likewise. Active Storage attempts to determine a file's content type from its information. Information technology falls back to the content type yous provide if it can't practise that.
@message . images . attach ( io: File . open ( '/path/to/file' ), filename: 'file.pdf' , content_type: 'application/pdf' ) You can bypass the content type inference from the information by passing in place: false along with the content_type.
@message . images . adhere ( io: File . open ( '/path/to/file' ), filename: 'file.pdf' , content_type: 'application/pdf' , place: false ) If y'all don't provide a content type and Agile Storage tin can't determine the file'due south content type automatically, it defaults to application/octet-stream.
iv Removing Files
To remove an attachment from a model, call purge on the attachment. If your awarding is set to use Active Job, removal tin exist done in the background instead by calling purge_later. Purging deletes the hulk and the file from the storage service.
# Synchronously destroy the avatar and actual resources files. user . avatar . purge # Destroy the associated models and actual resource files async, via Active Job. user . avatar . purge_later 5 Serving Files
Active Storage supports two ways to serve files: redirecting and proxying.
All Agile Storage controllers are publicly attainable by default. The generated URLs are difficult to estimate, only permanent by design. If your files require a college level of protection consider implementing Authenticated Controllers.
5.1 Redirect mode
To generate a permanent URL for a blob, y'all can laissez passer the blob to the url_for view helper. This generates a URL with the blob'southward signed_id that is routed to the hulk's RedirectController
url_for ( user . avatar ) # => /rails/active_storage/blobs/:signed_id/my-avatar.png The RedirectController redirects to the actual service endpoint. This indirection decouples the service URL from the actual one, and allows, for instance, mirroring attachments in unlike services for high-availability. The redirection has an HTTP expiration of 5 minutes.
To create a download link, use the rails_blob_{path|url} helper. Using this helper allows y'all to set the disposition.
rails_blob_path ( user . avatar , disposition: "zipper" ) To prevent XSS attacks, Agile Storage forces the Content-Disposition header to "attachment" for some kind of files. To modify this behaviour see the available configuration options in Configuring Runway Applications.
If yous need to create a link from outside of controller/view context (Background jobs, Cronjobs, etc.), you tin admission the rails_blob_path like this:
Rails . application . routes . url_helpers . rails_blob_path ( user . avatar , only_path: true ) 5.2 Proxy style
Optionally, files can be proxied instead. This means that your awarding servers will download file data from the storage service in response to requests. This tin can be useful for serving files from a CDN.
Yous can configure Active Storage to use proxying past default:
# config/initializers/active_storage.rb Runway . awarding . config . active_storage . resolve_model_to_route = :rails_storage_proxy Or if y'all want to explicitly proxy specific attachments in that location are URL helpers y'all can use in the class of rails_storage_proxy_path and rails_storage_proxy_url.
<%= image_tag rails_storage_proxy_path ( @user . avatar ) %> 5.2.1 Putting a CDN in front of Active Storage
Additionally, in order to apply a CDN for Active Storage attachments, you volition need to generate URLs with proxy mode so that they are served by your app and the CDN will cache the zipper without any extra configuration. This works out of the box because the default Active Storage proxy controller sets an HTTP header indicating to the CDN to cache the response.
You should also brand sure that the generated URLs employ the CDN host instead of your app host. In that location are multiple ways to achieve this, only in general information technology involves tweaking your config/routes.rb file so that you tin can generate the proper URLs for the attachments and their variations. Every bit an example, y'all could add this:
# config/routes.rb direct :cdn_image exercise | model , options | expires_in = options . delete ( :expires_in ) { ActiveStorage . urls_expire_in } if model . respond_to? ( :signed_id ) route_for ( :rails_service_blob_proxy , model . signed_id ( expires_in: expires_in ), model . filename , options . merge ( host: ENV [ 'CDN_HOST' ]) ) else signed_blob_id = model . blob . signed_id ( expires_in: expires_in ) variation_key = model . variation . primal filename = model . hulk . filename route_for ( :rails_blob_representation_proxy , signed_blob_id , variation_key , filename , options . merge ( host: ENV [ 'CDN_HOST' ]) ) end terminate and then generate routes like this:
<%= cdn_image_url ( user . avatar . variant ( resize_to_limit: [ 128 , 128 ])) %> v.3 Authenticated Controllers
All Active Storage controllers are publicly accessible by default. The generated URLs utilise a plain signed_id, making them difficult to guess but permanent. Anyone that knows the hulk URL volition exist able to admission it, fifty-fifty if a before_action in your ApplicationController would otherwise require a login. If your files require a higher level of protection, you can implement your own authenticated controllers, based on the ActiveStorage::Blobs::RedirectController, ActiveStorage::Blobs::ProxyController, ActiveStorage::Representations::RedirectController and ActiveStorage::Representations::ProxyController
To only permit an account to access their own logo yous could do the post-obit:
# config/routes.rb resources :account do resource :logo cease # app/controllers/logos_controller.rb class LogosController < ApplicationController # Through ApplicationController: # include Authenticate, SetCurrentAccount def show redirect_to Electric current . account . logo . url end end <%= image_tag account_logo_path %> Then you lot might desire to disable the Active Storage default routes with:
config . active_storage . draw_routes = false to prevent files being accessed with the publicly accessible URLs.
half dozen Downloading Files
Sometimes you demand to process a blob after it's uploaded—for example, to convert information technology to a different format. Use the attachment's download method to read a blob'southward binary data into retention:
binary = user . avatar . download You might want to download a blob to a file on disk so an external program (eastward.g. a virus scanner or media transcoder) tin can operate on it. Utilize the attachment's open method to download a blob to a tempfile on disk:
message . video . open do | file | system '/path/to/virus/scanner' , file . path # ... end Information technology's important to know that the file is non even so available in the after_create callback but in the after_create_commit only.
vii Analyzing Files
Agile Storage analyzes files in one case they've been uploaded by queuing a job in Agile Task. Analyzed files will shop additional information in the metadata hash, including analyzed: truthful. You can bank check whether a hulk has been analyzed by calling analyzed? on it.
Prototype assay provides width and pinnacle attributes. Video analysis provides these, as well as elapsing, angle, display_aspect_ratio, and video and audio booleans to signal the presence of those channels. Sound analysis provides duration and bit_rate attributes.
8 Displaying Images, Videos, and PDFs
Active Storage supports representing a variety of files. You lot can call representation on an attachment to display an image variant, or a preview of a video or PDF. Before calling representation, check if the zipper can be represented by calling representable?. Some file formats can't be previewed by Active Storage out of the box (e.g. Word documents); if representable? returns false y'all may desire to link to the file instead.
<ul> <% @bulletin . files . each do | file | %> <li> <% if file . representable? %> <%= image_tag file . representation ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]) %> <% else %> <%= link_to rails_blob_path ( file , disposition: "attachment" ) do %> <%= image_tag "placeholder.png" , alt: "Download file" %> <% end %> <% cease %> </li> <% end %> </ul> Internally, representation calls variant for images, and preview for previewable files. You can also call these methods directly.
8.1 Lazy vs Immediate Loading
By default, Active Storage will process representations lazily. This code:
image_tag file . representation ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]) Will generate an <img> tag with the src pointing to the ActiveStorage::Representations::RedirectController. The browser will make a request to that controller, which will return a 302 redirect to the file on the remote service (or in proxy mode, return the file contents). Loading the file lazily allows features similar single apply URLs to work without slowing downward your initial page loads.
This works fine for most cases.
If yous want to generate URLs for images immediately, you can call .candy.url:
image_tag file . representation ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]). processed . url The Active Storage variant tracker improves performance of this, by storing a record in the database if the requested representation has been processed before. Thus, the above lawmaking will only make an API call to the remote service (e.g. S3) once, and once a variant is stored, will use that. The variant tracker runs automatically, just can be disabled through config.active_storage.track_variants.
If yous're rendering lots of images on a page, the above example could result in N+1 queries loading all the variant records. To avoid these N+1 queries, use the named scopes on ActiveStorage::Attachment.
bulletin . images . with_all_variant_records . each do | file | image_tag file . representation ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]). processed . url cease 8.2 Transforming Images
Transforming images allows you to display the image at your pick of dimensions. To create a variation of an image, call variant on the attachment. Yous can laissez passer any transformation supported by the variant processor to the method. When the browser hits the variant URL, Active Storage will lazily transform the original blob into the specified format and redirect to its new service location.
<%= image_tag user . avatar . variant ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]) %> If a variant is requested, Agile Storage will automatically employ transformations depending on the paradigm's format:
-
Content types that are variable (equally dictated past
config.active_storage.variable_content_types) and not considered web images (equally dictated pastconfig.active_storage.web_image_content_types), will exist converted to PNG. -
If
qualityis not specified, the variant processor's default quality for the format volition be used.
Active Storage can use either Vips or MiniMagick as the variant processor. The default depends on your config.load_defaults target version, and the processor can exist changed past setting config.active_storage.variant_processor.
The ii processors are non fully uniform, and so when migrating an existing application between MiniMagick and Vips, some changes have to be made if using options that are format specific:
<!-- MiniMagick --> <%= image_tag user . avatar . variant ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ], format: :jpeg , sampling_factor: "4:2:0" , strip: true , interlace: "JPEG" , colorspace: "sRGB" , quality: 80 ) %> <!-- Vips --> <%= image_tag user . avatar . variant ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ], format: :jpeg , saver: { subsample_mode: "on" , strip: true , interlace: true , quality: 80 }) %> 8.3 Previewing Files
Some non-paradigm files can be previewed: that is, they can be presented as images. For case, a video file can be previewed by extracting its first frame. Out of the box, Active Storage supports previewing videos and PDF documents. To create a link to a lazily-generated preview, apply the attachment's preview method:
<%= image_tag message . video . preview ( resize_to_limit: [ 100 , 100 ]) %> To add together support for another format, add your own previewer. Run across the ActiveStorage::Preview documentation for more information.
9 Direct Uploads
Active Storage, with its included JavaScript library, supports uploading straight from the client to the deject.
nine.one Usage
-
Include
activestorage.jsin your application's JavaScript bundle.Using the asset pipeline:
//= crave activestorageUsing the npm package:
import * as ActiveStorage from " @rail/activestorage " ActiveStorage . start () -
Add
direct_upload: trueto your file field:<%= grade . file_field :attachments , multiple: true , direct_upload: true %>Or, if you aren't using a
FormBuilder, add the information attribute directly:<input blazon= file data-direct-upload-url= " <%= rails_direct_uploads_url %> " /> -
Configure CORS on tertiary-party storage services to allow direct upload requests.
-
That's information technology! Uploads begin upon form submission.
9.ii Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) configuration
To make direct uploads to a third-party service work, you'll need to configure the service to let cross-origin requests from your app. Consult the CORS documentation for your service:
- S3
- Google Deject Storage
- Azure Storage
Have care to allow:
- All origins from which your app is accessed
- The
PUTrequest method - The following headers:
-
Origin -
Content-Type -
Content-MD5 -
Content-Disposition(except for Azure Storage) -
x-ms-blob-content-disposition(for Azure Storage simply) -
ten-ms-blob-type(for Azure Storage only) -
Cache-Control(for GCS, only ifcache_controlis prepare)
-
No CORS configuration is required for the Disk service since it shares your app's origin.
9.two.1 Example: S3 CORS configuration
[ { "AllowedHeaders" : [ "*" ], "AllowedMethods" : [ "PUT" ], "AllowedOrigins" : [ "https://www.instance.com" ], "ExposeHeaders" : [ "Origin" , "Content-Type" , "Content-MD5" , "Content-Disposition" ], "MaxAgeSeconds" : 3600 } ] 9.2.2 Case: Google Deject Storage CORS configuration
[ { "origin" : [ "https://www.example.com" ], "method" : [ "PUT" ], "responseHeader" : [ "Origin" , "Content-Type" , "Content-MD5" , "Content-Disposition" ], "maxAgeSeconds" : 3600 } ] 9.ii.3 Example: Azure Storage CORS configuration
<Cors> <CorsRule> <AllowedOrigins>https://www.example.com</AllowedOrigins> <AllowedMethods>PUT</AllowedMethods> <AllowedHeaders>Origin, Content-Type, Content-MD5, x-ms-blob-content-disposition, 10-ms-blob-type</AllowedHeaders> <MaxAgeInSeconds>3600</MaxAgeInSeconds> </CorsRule> </Cors> 9.3 Straight upload JavaScript events
| Issue proper name | Result target | Result data (event.detail) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
directly-uploads:start | <form> | None | A form containing files for straight upload fields was submitted. |
direct-upload:initialize | <input> | {id, file} | Dispatched for every file afterwards form submission. |
directly-upload:start | <input> | {id, file} | A direct upload is starting. |
direct-upload:before-hulk-request | <input> | {id, file, xhr} | Before making a asking to your application for straight upload metadata. |
direct-upload:earlier-storage-request | <input> | {id, file, xhr} | Before making a request to store a file. |
direct-upload:progress | <input> | {id, file, progress} | As requests to store files progress. |
direct-upload:mistake | <input> | {id, file, error} | An error occurred. An alert will brandish unless this consequence is canceled. |
direct-upload:end | <input> | {id, file} | A direct upload has ended. |
directly-uploads:stop | <class> | None | All direct uploads have concluded. |
9.4 Case
Y'all can use these events to show the progress of an upload.
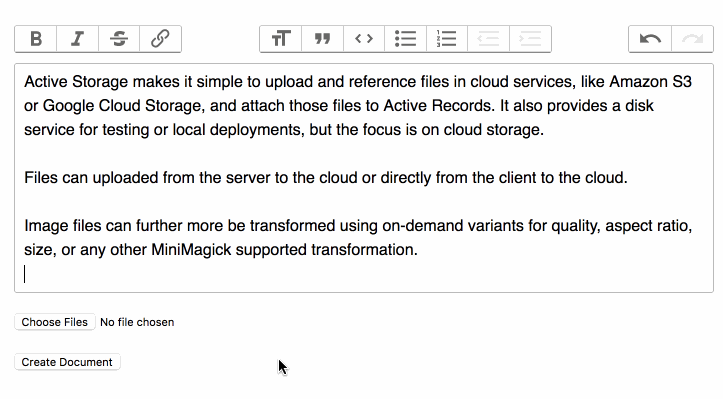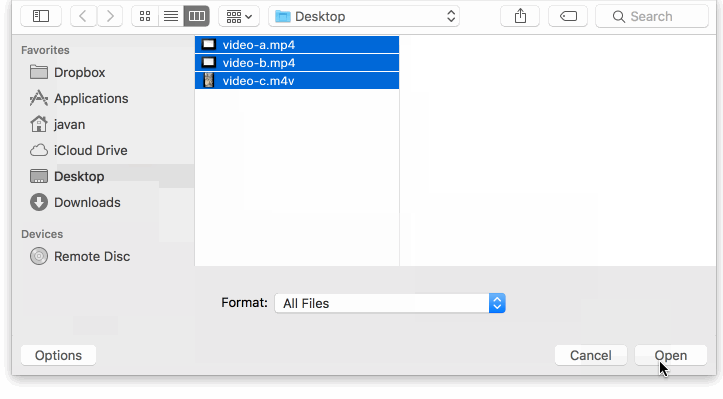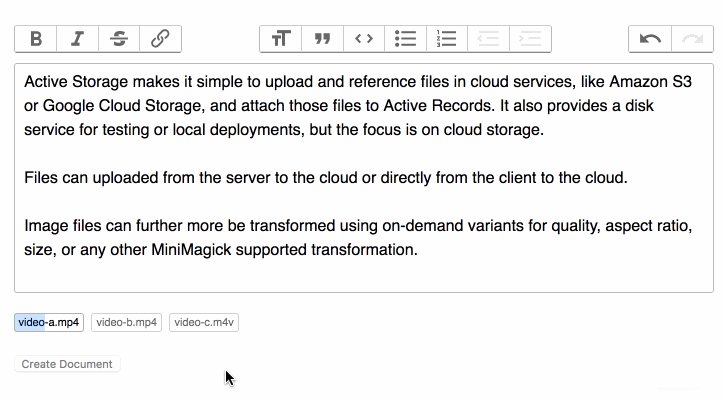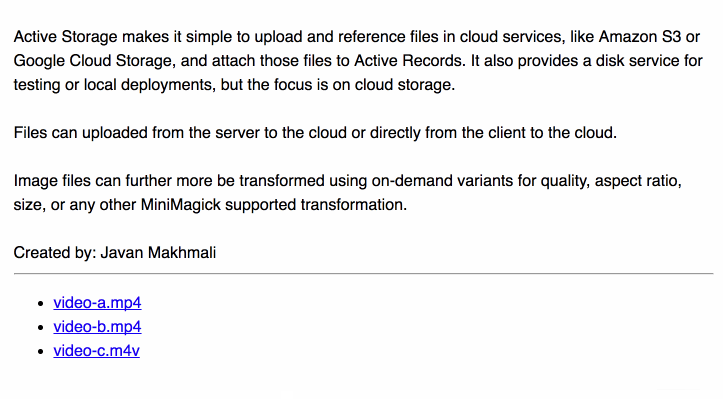
To show the uploaded files in a class:
// direct_uploads.js addEventListener ( " direct-upload:initialize " , event => { const { target , detail } = event const { id , file } = detail target . insertAdjacentHTML ( " beforebegin " , ` <div id="direct-upload- ${ id } " form="direct-upload direct-upload--awaiting"> <div id="direct-upload-progress- ${ id } " class="direct-upload__progress" style="width: 0%"></div> <bridge class="direct-upload__filename"></span> </div> ` ) target . previousElementSibling . querySelector ( `.directly-upload__filename` ). textContent = file . name }) addEventListener ( " straight-upload:first " , result => { const { id } = event . detail const element = document . getElementById ( `direct-upload- ${ id } ` ) element . classList . remove ( " straight-upload--pending " ) }) addEventListener ( " direct-upload:progress " , event => { const { id , progress } = result . item const progressElement = document . getElementById ( `straight-upload-progress- ${ id } ` ) progressElement . style . width = ` ${ progress } %` }) addEventListener ( " directly-upload:fault " , effect => { effect . preventDefault () const { id , error } = event . item const element = document . getElementById ( `direct-upload- ${ id } ` ) element . classList . add ( " straight-upload--fault " ) element . setAttribute ( " title " , error ) }) addEventListener ( " direct-upload:end " , effect => { const { id } = issue . particular const element = document . getElementById ( `straight-upload- ${ id } ` ) element . classList . add ( " direct-upload--complete " ) }) Add together styles:
/* direct_uploads.css */ .direct-upload { display : inline-block ; position : relative ; padding : 2px 4px ; margin : 0 3px 3px 0 ; border : 1px solid rgba ( 0 , 0 , 0 , 0.three ); border-radius : 3px ; font-size : 11px ; line-summit : 13px ; } .direct-upload--pending { opacity : 0.vi ; } .straight-upload__progress { position : absolute ; pinnacle : 0 ; left : 0 ; bottom : 0 ; opacity : 0.two ; background : #0076ff ; transition : width 120ms ease-out , opacity 60ms 60ms ease-in ; transform : translate3d ( 0 , 0 , 0 ); } .direct-upload--complete .straight-upload__progress { opacity : 0.4 ; } .straight-upload--fault { border-color : red ; } input [ type = file ][ information-direct-upload-url ][ disabled ] { display : none ; } 9.5 Integrating with Libraries or Frameworks
If y'all desire to use the Direct Upload feature from a JavaScript framework, or you want to integrate custom drag and driblet solutions, you can use the DirectUpload grade for this purpose. Upon receiving a file from your library of pick, instantiate a DirectUpload and phone call its create method. Create takes a callback to invoke when the upload completes.
import { DirectUpload } from " @rails/activestorage " const input = document . querySelector ( ' input[type=file] ' ) // Demark to file drop - use the ondrop on a parent element or utilise a // library like Dropzone const onDrop = ( event ) => { effect . preventDefault () const files = event . dataTransfer . files ; Array . from ( files ). forEach ( file => uploadFile ( file )) } // Demark to normal file selection input . addEventListener ( ' change ' , ( result ) => { Array . from ( input . files ). forEach ( file => uploadFile ( file )) // you might clear the selected files from the input input . value = nix }) const uploadFile = ( file ) => { // your form needs the file_field direct_upload: truthful, which // provides information-straight-upload-url const url = input . dataset . directUploadUrl const upload = new DirectUpload ( file , url ) upload . create (( mistake , blob ) => { if ( fault ) { // Handle the error } else { // Add an accordingly-named hidden input to the form with a // value of hulk.signed_id so that the blob ids will exist // transmitted in the normal upload menses const hiddenField = document . createElement ( ' input ' ) hiddenField . setAttribute ( " type " , " hidden " ); hiddenField . setAttribute ( " value " , blob . signed_id ); hiddenField . name = input . name document . querySelector ( ' form ' ). appendChild ( hiddenField ) } }) } If you demand to runway the progress of the file upload, you lot tin can pass a third parameter to the DirectUpload constructor. During the upload, DirectUpload will call the object's directUploadWillStoreFileWithXHR method. You can then demark your own progress handler on the XHR.
import { DirectUpload } from " @track/activestorage " class Uploader { constructor ( file , url ) { this . upload = new DirectUpload ( this . file , this . url , this ) } upload ( file ) { this . upload . create (( error , blob ) => { if ( mistake ) { // Handle the mistake } else { // Add together an appropriately-named hidden input to the form // with a value of blob.signed_id } }) } directUploadWillStoreFileWithXHR ( request ) { request . upload . addEventListener ( " progress " , event => this . directUploadDidProgress ( event )) } directUploadDidProgress ( event ) { // Use event.loaded and upshot.total to update the progress bar } } Using Direct Uploads can sometimes effect in a file that uploads, but never attaches to a record. Consider purging unattached uploads.
ten Testing
Use fixture_file_upload to test uploading a file in an integration or controller examination. Rails handles files similar any other parameter.
class SignupController < ActionDispatch :: IntegrationTest test "can sign up" practise post signup_path , params: { name: "David" , avatar: fixture_file_upload ( "david.png" , "prototype/png" ) } user = User . social club ( :created_at ). last affirm user . avatar . attached? cease end 10.1 Discarding files created during tests
x.1.1 System tests
System tests clean up test data by rolling back a transaction. Because destroy is never called on an object, the attached files are never cleaned up. If you lot want to articulate the files, you can do it in an after_teardown callback. Doing it here ensures that all connections created during the test are complete and yous won't receive an error from Active Storage proverb it tin can't observe a file.
form ApplicationSystemTestCase < ActionDispatch :: SystemTestCase # ... def after_teardown super FileUtils . rm_rf ( ActiveStorage :: Blob . service . root ) end # ... terminate If you're using parallel tests and the DiskService, y'all should configure each procedure to utilize its ain folder for Active Storage. This style, the teardown callback will merely delete files from the relevant process' tests.
class ApplicationSystemTestCase < ActionDispatch :: SystemTestCase # ... parallelize_setup do | i | ActiveStorage :: Blob . service . root = " #{ ActiveStorage :: Blob . service . root } - #{ i } " end # ... terminate If your system tests verify the deletion of a model with attachments and you lot're using Active Job, set your exam surroundings to use the inline queue adapter then the purge chore is executed immediately rather at an unknown time in the futurity.
# Utilise inline chore processing to make things happen immediately config . active_job . queue_adapter = :inline 10.1.2 Integration tests
Similarly to Organisation Tests, files uploaded during Integration Tests will not be automatically cleaned up. If you want to articulate the files, y'all can exercise information technology in an teardown callback.
class ActionDispatch::IntegrationTest def after_teardown super FileUtils . rm_rf ( ActiveStorage :: Blob . service . root ) end end If yous're using parallel tests and the Deejay service, you should configure each procedure to use its own folder for Active Storage. This way, the teardown callback volition only delete files from the relevant process' tests.
course ActionDispatch::IntegrationTest parallelize_setup exercise | i | ActiveStorage :: Hulk . service . root = " #{ ActiveStorage :: Blob . service . root } - #{ i } " stop end ten.2 Calculation attachments to fixtures
You tin can add attachments to your existing fixtures. First, you'll want to create a separate storage service:
# config/storage.yml test_fixtures : service : Disk root : <%= Rails.root.join("tmp/storage_fixtures") %> This tells Active Storage where to "upload" fixture files to, so it should be a temporary directory. By making information technology a different directory to your regular test service, you can separate fixture files from files uploaded during a test.
Adjacent, create fixture files for the Agile Storage classes:
# active_storage/attachments.yml david_avatar : name : avatar record : david (User) blob : david_avatar_blob # active_storage/blobs.yml david_avatar_blob : <%= ActiveStorage::FixtureSet.blob filename : " david.png" , service_name : " test_fixtures" % > Then put a file in your fixtures directory (the default path is exam/fixtures/files) with the corresponding filename. Meet the ActiveStorage::FixtureSet docs for more than data.
One time everything is fix, yous'll be able to access attachments in your tests:
class UserTest < ActiveSupport :: TestCase def test_avatar avatar = users ( :david ). avatar assert avatar . fastened? assert_not_nil avatar . download assert_equal yard , avatar . byte_size end end 10.2.1 Cleaning up fixtures
While files uploaded in tests are cleaned up at the end of each test, you simply need to clean upwardly fixture files once: when all your tests complete.
If you're using parallel tests, call parallelize_teardown:
class ActiveSupport::TestCase # ... parallelize_teardown exercise | i | FileUtils . rm_rf ( ActiveStorage :: Blob . services . fetch ( :test_fixtures ). root ) end # ... end If you lot're not running parallel tests, utilise Minitest.after_run or the equivalent for your test framework (e.1000. later(:suite) for RSpec):
# test_helper.rb Minitest . after_run practice FileUtils . rm_rf ( ActiveStorage :: Hulk . services . fetch ( :test_fixtures ). root ) cease xi Implementing Support for Other Deject Services
If y'all need to support a deject service other than these, you will demand to implement the Service. Each service extends ActiveStorage::Service by implementing the methods necessary to upload and download files to the cloud.
12 Purging Unattached Uploads
There are cases where a file is uploaded only never fastened to a record. This tin can happen when using Straight Uploads. You lot can query for unattached records using the unattached scope. Below is an example using a custom rake job.
namespace :active_storage do desc "Purges unattached Active Storage blobs. Run regularly." job purge_unattached: :environment do ActiveStorage :: Blob . unattached . where ( "active_storage_blobs.created_at <= ?" , 2 . days . ago ). find_each ( & :purge_later ) cease finish The query generated by ActiveStorage::Blob.unattached tin can exist irksome and potentially disruptive on applications with larger databases.
Feedback
Yous're encouraged to help improve the quality of this guide.
Please contribute if you meet any typos or factual errors. To go started, y'all can read our documentation contributions section.
You may as well find incomplete content or stuff that is non up to date. Delight practice add whatsoever missing documentation for chief. Make sure to check Edge Guides first to verify if the issues are already stock-still or non on the main branch. Check the Ruby on Rails Guides Guidelines for style and conventions.
If for whatever reason you spot something to gear up merely cannot patch it yourself, please open up an issue.
And terminal but not least, whatever kind of discussion regarding Blood-red on Rails documentation is very welcome on the rubyonrails-docs mailing listing.
Source: https://edgeguides.rubyonrails.org/active_storage_overview.html
0 Response to "Rails Form Drag and Drop Photo Uploader"
Post a Comment