Blood Draw via Peripheral Line
| Ensure that patient and health care provider safety standards are met during this procedure including:
| |
| |
| PROCEDURE | |
| 1. | Obtain Order
Change the ethanol Swab Cap(TM) cap after each access. Draw blood sample through the needless access cap. Change this cap if if is contaminated or has residual blood. Note: The needless system reduces the risk for stopcock contamination and needlestick injuries. Collection of backflush solution into a disposable blood tube reduces exposure of health care providers to blood products. Back-flushing reduces potential to introduce pathogens. Arterial lines are frequently the source for blood stream infection include central line associated blood stream infections. |
| 2. | Obtain Equipment Perform hand hygiene before donning non-sterile gloves. Assess risk for need of a face shield Collect necessary equipment:
Note: If you are not collecting any blood into vacuum tubes (i.e, blood gases, glucometer samples or point-of-care testing), a syringe can be used to collect the discard sample and to back flush. |
| 3. | Prepare Equipment and Environment
Blood sampling from an arterial line reduces patient discomfort from needle sticks, however, patients should be advised that they may feel a warm sensation in their extremity during line flushing. |
| 4. | Connect Blood Drawing System
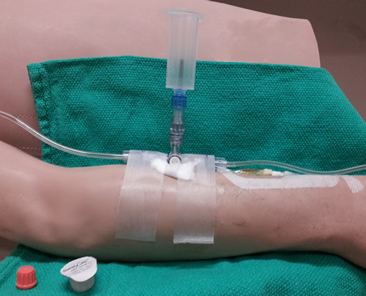
The Centre for Disease Control (CDC) recommends 70% alcohol or an or an iodophor for cleansing injection sites. Chlorhexidine adheres to provide prolonged gm positive antimicrobial properties. 2. Connect vactainer with sampling needle to luer-lock sampling port as shown in Figure 1.01. 3. Begin with 3-way stopcock positioned with prong toward the sampling port (this is off to sampling port). |
| 5. | Collect Discard Sample (Artrial Lines)
Note: If you are not collecting any blood tubes, you can collect discard sample into an extra syringe. |
| 6. | Collect Discard Sample (Venous Samples)
Consider IV contamination for any patient with unusual electrolyte or lab values. TPN can significantly contaminate blood samples. |
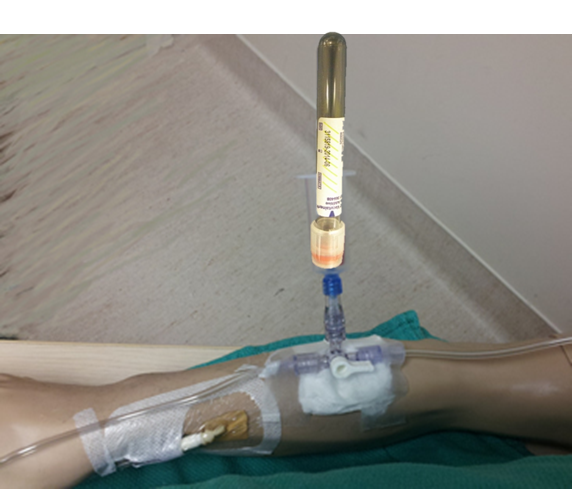
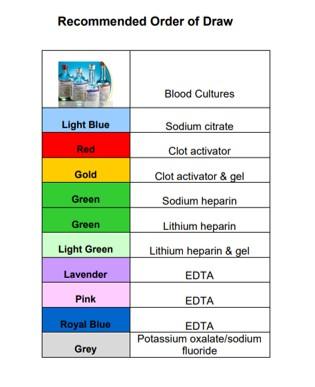
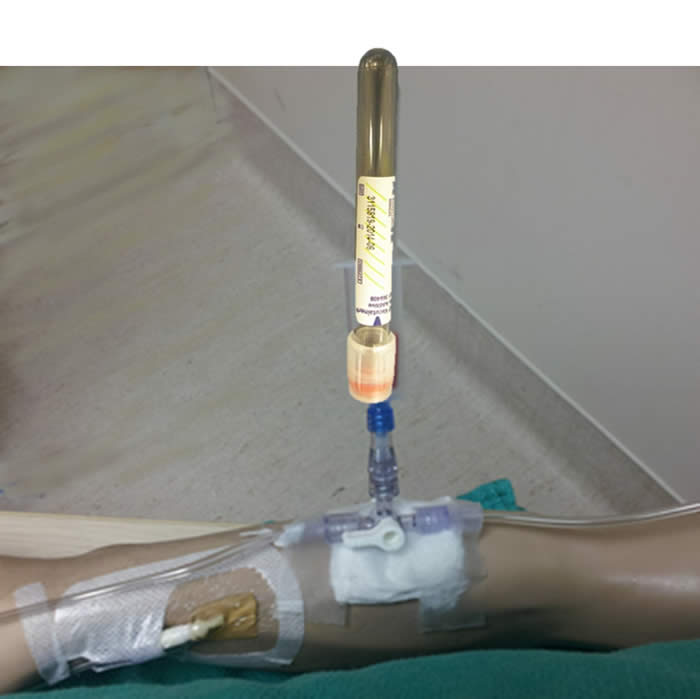
| 7. | Collect Blood Samples to Prevent Dilution or Contamination with IV Fluids or Vaccum Tube Contents Order of Draw When drawing blood from an indwelling line, the INR/PTT should be drawn AFTER blood gases to prevent contamination of the PTT from the heparinized blood gas syringe. Although we do not routinely heparinize our hemodynamic circuits anymore, any PTT drawn from a heparinized line should be drawn after at least a 5 ml discard. The recommended order of blood tube collection is shown in Figure 1.03. Position Stopcock to 45 Degrees Between All Samples/Tube Changes
|
| 8. | Flush the Patient Catheter
|
| 9. | Backflush the Stopcock
|
| 10. | Label Specimens
|
| 11. | Document
|
References:
http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/hip
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr5110a1.htm
http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/bbp/sharps.html
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmw.htm/rr5110a1.htm
Gillies D, O'Riordan L, Wallen M, et al. Optimal timing for intravenous administration set replacement. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005;(4):CD003588.
Luebke, M., et al. (1998). Am J Infection Control, 26: pp. 437-441.
Plott, R., Wagner, R., Tyring, S. (1990). Archive Dermatology, 126: pp 1441-1444.
Salzman, M., Isenberg, H., Rubin, L. (1993). Journal of Clinical. Microbiology, 31: pp. 475-479
Developed by: Brenda Morgan, CNS, CCTC 1988
Revised: June 30, 2016, Reviewed: February 5, 2021
Blood Draw via Peripheral Line
Source: https://www.lhsc.on.ca/critical-care-trauma-centre/blood-sampling-from-an-indwelling-line

0 Response to "Blood Draw via Peripheral Line"
Post a Comment